Hackers use new HexStrike-AI tool to rapidly exploit n-day flaws

Hackers are increasingly using a new AI-powered offensive security framework called HexStrike-AI in real attacks to exploit newly disclosed n-day flaws.
This activity is reported by CheckPoint Research, which observed significant chatter on the dark web around HexStrike-AI, associated with the rapid weaponization of newly disclosed Citrix vulnerabilities, including CVE-2025-7775, CVE-2025-7776, and CVE-2025-8424.
According to ShadowServer Foundation's data, nearly 8,000 endpoints remain vulnerable to CVE-2025-7775 as of September 2, 2025, down from 28,000 the previous week.
Power in the wrong hands
HexStrike-AI is a legitimate red teaming tool created by cybersecurity researcher Muhammad Osama, which enables the integration of AI agents to autonomously run over 150 cybersecurity tools for automated penetration testing and vulnerability discovery.
"HexStrike AI operates with human-in-the-loop interaction through external LLMs via MCP, creating a continuous cycle of prompts, analysis, execution, and feedback," reads its creator's description.
HexStrike-AI's client features a retry logic and recovery handling to mitigate the effects of failures in any individual step on its complex operations. Instead, it automatically retries or adjusts its configuration until the operation completes successfully.
The tool has been open-source and available on GitHub for the last month, where it has already garnered 1,800 stars and over 400 forks.
Unfortunately, it has also attracted the attention of hackers who have begun to use it in their attacks.
According to CheckPoint, hackers started discussing the tool on hacking forums, where they discussed how to deploy HexStrike-AI to exploit the mentioned Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway zero-day vulnerabilities within hours of their disclosure.
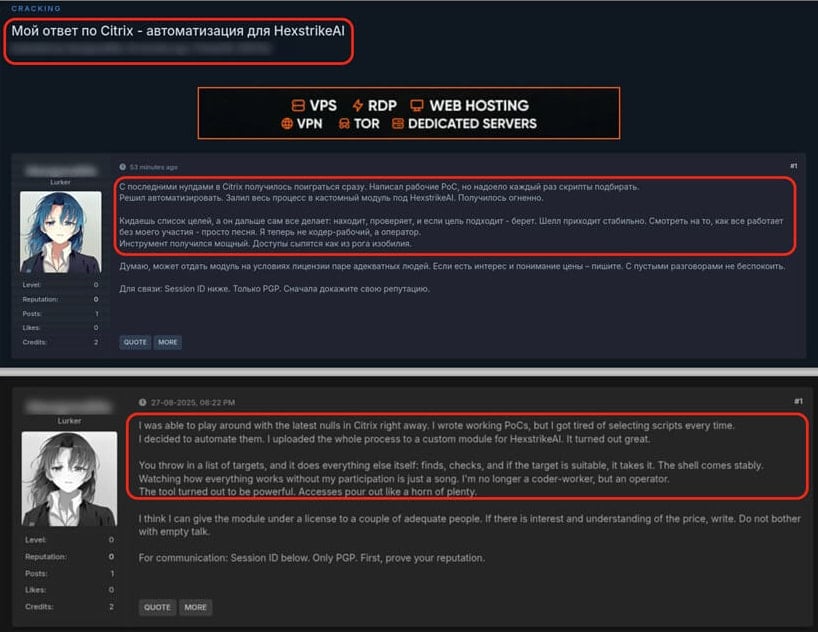
Threat actors reportedly used it to achieve unauthenticated remote code execution through CVE-2025-7775 and then drop webshells on compromised appliances, with some offering compromised NetScaler instances for sale.
CheckPoint believes it's likely the attackers used the new pentesting framework to automate their exploitation chain, scanning for vulnerable instances, crafting exploits, delivering payloads, and maintaining persistence.
Although the actual involvement of HexStrike-AI in these attacks hasn't been confirmed, such a level of automation could reduce the n-day flaw exploitation times from several days down to a few minutes.
Such a development would leave system administrators with an already small patching window and even less time before attacks begin.
"The window between disclosure and mass exploitation shrinks dramatically." commented Check Point on a recently disclosed Citrix flaw.
"CVE-2025-7775 is already being exploited in the wild, and with Hexstrike-AI, the volume of attacks will only increase in the coming days."
Although speedy patching remains crucial, this paradigm shift brought by AI-powered attack frameworks makes it even more important to maintain a strong, holistic security stance.
Check Point recommends defenders focus on early warning through threat intelligence, AI-driven defenses, and adaptive detection.






